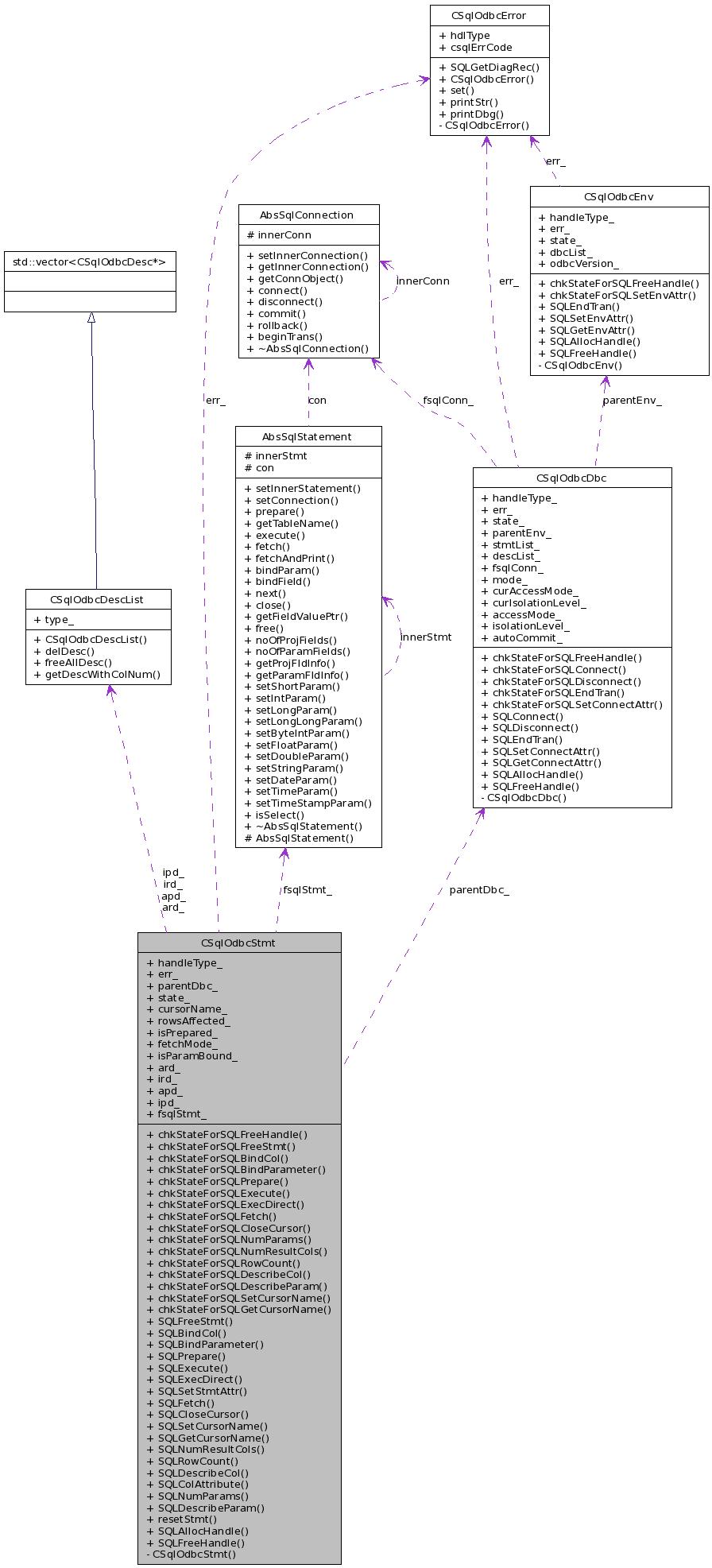
#include <odbcStmt.h>
Collaboration diagram for CSqlOdbcStmt:

Definition at line 26 of file odbcStmt.h.
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLBindCol | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 158 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLBindCol().
00159 { 00160 switch( state_ ) 00161 { 00162 case S0: 00163 case S1: 00164 case S2: 00165 case S3: 00166 case S4: 00167 case S5: 00168 case S6: 00169 case S7: break; 00170 case S8: 00171 case S9: 00172 case S10: 00173 case S11: 00174 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00175 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00176 } 00177 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00178 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLBindParameter | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 179 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLBindParameter().
00180 { 00181 switch( state_ ) 00182 { 00183 case S0: 00184 case S1: 00185 case S2: 00186 case S3: 00187 case S4: 00188 case S5: 00189 case S6: 00190 case S7: break; 00191 case S8: 00192 case S9: 00193 case S10: 00194 case S11: 00195 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00196 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00197 } 00198 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00199 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLCloseCursor | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 295 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLCloseCursor().
00296 { 00297 switch( state_ ) 00298 { 00299 case S0: 00300 case S1: 00301 case S2: 00302 case S3: 00303 case S4: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00304 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00305 case S5: 00306 case S6: 00307 case S7: break; 00308 case S8: 00309 case S9: 00310 case S10: 00311 case S11: 00312 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00313 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00314 } 00315 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00316 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

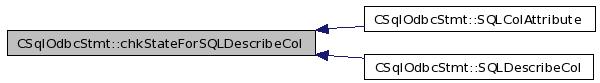
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLDescribeCol | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 408 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLColAttribute(), and SQLDescribeCol().
00409 { 00410 switch( state_ ) 00411 { 00412 case S4: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00413 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00414 00415 case S3: 00416 case S5: 00417 case S6: 00418 case S7: break; 00419 00420 case S0: 00421 case S1: 00422 case S2: 00423 00424 case S8: 00425 case S9: 00426 case S10: 00427 case S11: 00428 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00429 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00430 } 00431 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00432 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLDescribeParam | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 457 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLDescribeParam().
00458 { 00459 switch( state_ ) 00460 { 00461 case S2: 00462 case S3:break; 00463 case S0: 00464 case S1: 00465 case S5: 00466 case S6: 00467 case S7: 00468 case S8: 00469 case S9: 00470 case S10: 00471 case S11: 00472 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00473 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00474 } 00475 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00476 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLExecDirect | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 247 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLExecDirect().
00248 { 00249 switch( state_ ) 00250 { 00251 case S0: 00252 case S1: 00253 case S2: 00254 case S3: 00255 case S4: break; 00256 00257 case S5: 00258 case S6: 00259 case S7: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00260 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00261 00262 case S8: 00263 case S9: 00264 case S10: 00265 case S11: 00266 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00267 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00268 } 00269 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00270 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLExecute | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 223 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLExecute().
00224 { 00225 switch( state_ ) 00226 { 00227 case S2: 00228 case S3: 00229 case S4: break; 00230 00231 case S5: 00232 case S6: 00233 case S7: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00234 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00235 00236 case S0: 00237 case S1: 00238 case S8: 00239 case S9: 00240 case S10: 00241 case S11: 00242 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00243 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00244 } 00245 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00246 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLFetch | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 271 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, ERROR_NOT_PREPAREDSTMT, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLFetch().
00272 { 00273 switch( state_ ) 00274 { 00275 case S0: 00276 case S1: 00277 case S2: 00278 case S3: err_.set( ERROR_NOT_PREPAREDSTMT ); 00279 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00280 case S4: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00281 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00282 case S5: 00283 case S6: 00284 case S7: break; 00285 00286 case S8: 00287 case S9: 00288 case S10: 00289 case S11: 00290 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00291 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00292 } 00293 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00294 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
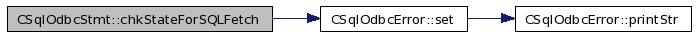
Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLFreeHandle | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 116 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
00117 { 00118 switch( state_ ) 00119 { 00120 case S0: 00121 case S1: 00122 case S2: 00123 case S3: 00124 case S4: 00125 case S5: 00126 case S6: 00127 case S7: break; 00128 case S8: 00129 case S9: 00130 case S10: 00131 case S11: 00132 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00133 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00134 } 00135 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00136 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLFreeStmt | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 137 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLFreeStmt().
00138 { 00139 switch( state_ ) 00140 { 00141 case S0: 00142 case S1: 00143 case S2: 00144 case S3: 00145 case S4: 00146 case S5: 00147 case S6: 00148 case S7: break; 00149 case S8: 00150 case S9: 00151 case S10: 00152 case S11: 00153 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00154 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00155 } 00156 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00157 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:
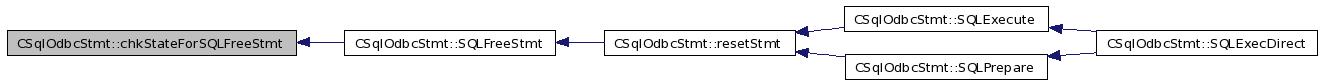
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLGetCursorName | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 317 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLGetCursorName().
00318 { 00319 switch( state_ ) 00320 { 00321 case S0: 00322 case S1: 00323 case S2: 00324 case S3: 00325 case S4: 00326 case S5: 00327 case S6: 00328 case S7: break; 00329 00330 case S8: 00331 case S9: 00332 case S10: 00333 case S11: 00334 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00335 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00336 } 00337 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00338 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLNumParams | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 433 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLNumParams().
00434 { 00435 switch( state_ ) 00436 { 00437 00438 case S0: err_.set(ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00439 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00440 case S2: 00441 case S3: 00442 case S4: 00443 case S5: 00444 case S6: 00445 case S7: break; 00446 case S1: 00447 case S8: 00448 case S9: 00449 case S10: 00450 case S11: 00451 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00452 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00453 } 00454 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00455 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLNumResultCols | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 362 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLNumResultCols().
00363 { 00364 switch( state_ ) 00365 { 00366 case S2: 00367 case S3: 00368 case S4: 00369 case S5: 00370 case S6: 00371 case S7: break; 00372 00373 case S0: 00374 case S1: 00375 00376 case S8: 00377 case S9: 00378 case S10: 00379 case S11: 00380 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00381 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00382 } 00383 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00384 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLPrepare | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 200 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLPrepare().
00201 { 00202 switch( state_ ) 00203 { 00204 case S0: 00205 case S1: 00206 case S2: 00207 case S3: 00208 case S4: break; 00209 00210 case S5: 00211 case S6: 00212 case S7: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00213 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00214 case S8: 00215 case S9: 00216 case S10: 00217 case S11: 00218 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00219 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00220 } 00221 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00222 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:
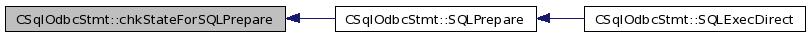
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLRowCount | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 385 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLRowCount().
00386 { 00387 switch( state_ ) 00388 { 00389 case S4: 00390 case S5: 00391 case S6: break; 00392 00393 case S0: 00394 case S1: 00395 case S2: 00396 case S3: 00397 00398 case S7: 00399 case S8: 00400 case S9: 00401 case S10: 00402 case S11: 00403 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00404 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00405 } 00406 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00407 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::chkStateForSQLSetCursorName | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 339 of file odbcState.cxx.
References err_, ERROR_FUNCSEQ, ERROR_INVCURSTATE, S0, S1, S10, S11, S12, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLSetCursorName().
00340 { 00341 switch( state_ ) 00342 { 00343 case S0: 00344 case S1: 00345 case S2: 00346 case S3: break; 00347 00348 case S4: 00349 case S5: 00350 case S6: 00351 case S7: 00352 case S8: err_.set( ERROR_INVCURSTATE ); 00353 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00354 case S9: 00355 case S10: 00356 case S11: 00357 case S12: err_.set( ERROR_FUNCSEQ ); 00358 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00359 } 00360 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00361 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

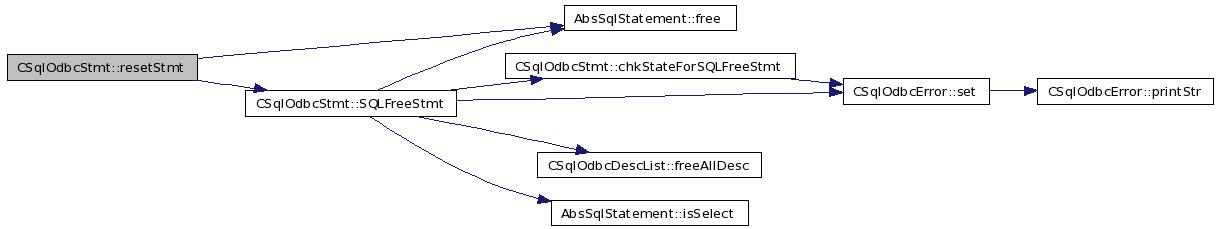
| void CSqlOdbcStmt::resetStmt | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1455 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References AbsSqlStatement::free(), fsqlStmt_, isPrepared_, S1, SQL_CLOSE, SQL_RESET_PARAMS, SQL_UNBIND, SQLFreeStmt(), and state_.
Referenced by SQLExecute(), and SQLPrepare().
01456 { 01457 SQLFreeStmt( SQL_CLOSE ); 01458 SQLFreeStmt( SQL_UNBIND ); 01459 SQLFreeStmt( SQL_RESET_PARAMS ); 01460 if (fsqlStmt_) fsqlStmt_->free(); 01461 delete fsqlStmt_; 01462 fsqlStmt_ = NULL; 01463 isPrepared_ = false; 01464 state_ = S1; 01465 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:

Definition at line 33 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References C4, C5, ERROR_CONNOTOPEN, ERROR_MEMALLOC, globalError, isValidHandle(), CSqlOdbcError::printStr(), CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_HANDLE_DBC, SQL_INVALID_HANDLE, SQL_OV_ODBC3, and SQL_SUCCESS.
Referenced by SQLAllocHandle(), and SQLAllocStmt().
00036 { 00037 CSqlOdbcDbc *inputDbc = (CSqlOdbcDbc*) inputHandle; 00038 00039 // Is Dbc valid ? 00040 if( isValidHandle( inputDbc, SQL_HANDLE_DBC ) != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00041 return( SQL_INVALID_HANDLE ); 00042 00043 // Is Dbc connected ? 00044 if( inputDbc->state_ < C4 ) 00045 { 00046 globalError.set( ERROR_CONNOTOPEN ); 00047 globalError.printStr( SQL_OV_ODBC3 ); 00048 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00049 } 00050 00051 // Allocate Statement object. 00052 *outputHandle = (SQLHANDLE*) new CSqlOdbcStmt; 00053 if( *outputHandle == NULL ) 00054 { 00055 globalError.set( ERROR_MEMALLOC ); 00056 globalError.printStr( SQL_OV_ODBC3 ); 00057 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00058 } 00059 00060 // Initialize relation b/w Stmt and Dbc 00061 inputDbc->stmtList_.insert( inputDbc->stmtList_.begin(), (CSqlOdbcStmt*) *outputHandle ); 00062 if( inputDbc->state_ <= C4 ) 00063 inputDbc->state_ = C5; 00064 ((CSqlOdbcStmt*) *outputHandle)->parentDbc_ = inputDbc; 00065 //CSqlOdbcError::printDbg("proxy:stmt:setConnection"); 00066 //((CSqlOdbcStmt*) *outputHandle)->fsqlStmt_->setConnection( inputDbc->fsqlConn_ ); 00067 00068 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00069 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLBindCol | ( | SQLUSMALLINT | columnNumber, | |
| SQLSMALLINT | targetType, | |||
| SQLPOINTER | targetValue, | |||
| SQLINTEGER | bufferLength, | |||
| SQLINTEGER * | ind | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 200 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References ard_, chkStateForSQLBindCol(), CSqlOdbcDesc::col_, CSqlOdbcDesc::cType_, CSqlOdbcDesc::dataPtr_, CSqlOdbcDescList::delDesc(), err_, ERROR_BUFLEN, ERROR_COLNUM, ERROR_INVBUFTYPE, getCSqlType(), CSqlOdbcDescList::getDescWithColNum(), getInputBuffer(), CSqlOdbcDesc::indPtr_, ird_, isValidCType(), CSqlOdbcDesc::length_, NO_ERR, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_C_BINARY, SQL_C_CHAR, SQL_ERROR, SQL_NTS, and SQL_SUCCESS.
00206 { 00207 CSqlOdbcDesc *bindDesc = 0; 00208 CSqlOdbcDesc *inputDesc = 0; 00209 SQLRETURN found = SQL_ERROR; 00210 00211 // Start with NO_ERR 00212 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00213 00214 // Can we proceed ? 00215 if( chkStateForSQLBindCol() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00216 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00217 00218 // Invalid Buffer Length. 00219 switch( targetType ) 00220 { 00221 // switch is in order to support more types. 00222 case SQL_C_CHAR: 00223 if( bufferLength < 0 && bufferLength != SQL_NTS ) 00224 { 00225 err_.set( ERROR_BUFLEN ); 00226 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00227 } 00228 break; 00229 case SQL_C_BINARY: 00230 if( bufferLength < 0 && bufferLength != SQL_NTS ) 00231 { 00232 err_.set( ERROR_BUFLEN ); 00233 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00234 } 00235 break; 00236 } 00237 00238 // Invalid Column Number 00239 if( columnNumber < 1 ) 00240 { 00241 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 00242 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00243 } 00244 00245 // Get the Descriptor if already exists 00246 found = ard_.getDescWithColNum( columnNumber , &bindDesc ); 00247 00248 // UNBIND 00249 if( targetValue == 0 ) 00250 { 00251 if( found != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00252 { 00253 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 00254 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00255 } 00256 ard_.delDesc( bindDesc ); // UNBIND 00257 00258 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00259 } 00260 00261 // Validate target Type, Value and Column no. 00262 if( targetValue == 0 || isValidCType( targetType ) != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00263 { 00264 err_.set( ERROR_INVBUFTYPE ); 00265 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00266 } 00267 00268 // Add new descriptor 00269 if( found != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00270 { 00271 bindDesc = new CSqlOdbcDesc(); 00272 ard_.insert( ard_.begin(), bindDesc ); 00273 } 00274 00275 // Initialize Descriptor. 00276 bindDesc->col_ = columnNumber; 00277 bindDesc->cType_ = targetType; 00278 bindDesc->dataPtr_ = targetValue; 00279 bindDesc->length_ = (SQLUINTEGER) bufferLength; 00280 bindDesc->indPtr_ = (SQLPOINTER) ind; 00281 00282 found = ird_.getDescWithColNum( columnNumber , &inputDesc ); 00283 00284 // Add new descriptor 00285 if( found != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00286 { 00287 inputDesc = new CSqlOdbcDesc(); 00288 ird_.insert(ird_.begin(),inputDesc); 00289 } 00290 00291 // Initialize input Descriptor. 00292 DataType sourceType = getCSqlType( targetType ); 00293 inputDesc->col_ = columnNumber; 00294 inputDesc->cType_ = targetType; 00295 getInputBuffer(&inputDesc->dataPtr_ ,sourceType,(SQLUINTEGER) bufferLength); 00296 inputDesc->length_ = (SQLUINTEGER) bufferLength; 00297 inputDesc->indPtr_ = (SQLPOINTER) ind; 00298 00299 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00300 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLBindParameter | ( | SQLUSMALLINT | parameterNumber, | |
| SQLSMALLINT | inputOutputType, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT | valueType, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT | parameterType, | |||
| SQLUINTEGER | lengthPrecision, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT | parameterScale, | |||
| SQLPOINTER | parameterValue, | |||
| SQLINTEGER | bufferLength, | |||
| SQLINTEGER * | ind | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 355 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References apd_, chkStateForSQLBindParameter(), CSqlOdbcDesc::col_, CSqlOdbcDesc::cType_, CSqlOdbcDesc::dataPtr_, err_, ERROR_BUFLEN, ERROR_COLNUM, ERROR_INV_PARAMTYPE, ERROR_INVBUFTYPE, getCSqlType(), CSqlOdbcDescList::getDescWithColNum(), CSqlOdbcDesc::indPtr_, ipd_, isValidCType(), isValidSQLType(), CSqlOdbcDesc::length_, NO_ERR, CSqlOdbcDesc::paramType_, CSqlOdbcDesc::precision_, CSqlOdbcDesc::scale_, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_C_BINARY, SQL_C_CHAR, SQL_ERROR, SQL_NTS, SQL_PARAM_INPUT, SQL_PARAM_INPUT_OUTPUT, SQL_PARAM_OUTPUT, SQL_SUCCESS, and CSqlOdbcDesc::sqlType_.
00365 { 00366 CSqlOdbcDesc *bindDesc = 0; 00367 CSqlOdbcDesc *inputDesc =0; 00368 SQLRETURN found; 00369 00370 // Start with NO_ERR 00371 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00372 00373 // Can we proceed ? 00374 if( chkStateForSQLBindParameter() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00375 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00376 00377 // Invalid Buffer Length. 00378 switch( valueType ) 00379 { 00380 // switch is in order to support more types. 00381 case SQL_C_CHAR: 00382 if( bufferLength < 0 && bufferLength != SQL_NTS ) 00383 { 00384 err_.set( ERROR_BUFLEN ); 00385 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00386 } 00387 break; 00388 case SQL_C_BINARY: 00389 if( bufferLength < 0 && bufferLength != SQL_NTS ) 00390 { 00391 err_.set( ERROR_BUFLEN ); 00392 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00393 } 00394 break; 00395 } 00396 00397 // Validate parameters 00398 switch( inputOutputType ) 00399 { 00400 case SQL_PARAM_INPUT: 00401 case SQL_PARAM_OUTPUT: 00402 case SQL_PARAM_INPUT_OUTPUT: break; 00403 default: err_.set( ERROR_INV_PARAMTYPE ); 00404 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00405 } 00406 if( isValidCType( valueType ) != SQL_SUCCESS || 00407 isValidSQLType( parameterType ) != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00408 { 00409 err_.set( ERROR_INVBUFTYPE ); 00410 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00411 } 00412 if( parameterNumber < 1 ) 00413 { 00414 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 00415 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00416 } 00417 00418 // Get the Descriptor if already exists 00419 found = apd_.getDescWithColNum( parameterNumber , &bindDesc ); 00420 if( found != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00421 { 00422 bindDesc = new CSqlOdbcDesc(); 00423 apd_.insert( apd_.end(), bindDesc ); 00424 // Initialize Descriptor. 00425 bindDesc->col_ = parameterNumber; 00426 bindDesc->paramType_ = inputOutputType; 00427 bindDesc->cType_ = valueType; 00428 bindDesc->sqlType_ = parameterType; 00429 bindDesc->dataPtr_ = parameterValue; 00430 bindDesc->length_ = (SQLUINTEGER) bufferLength; 00431 bindDesc->precision_ =(short) lengthPrecision; 00432 bindDesc->scale_ = parameterScale; 00433 bindDesc->indPtr_ = (SQLPOINTER) ind; 00434 } 00435 found = ipd_.getDescWithColNum (parameterNumber, &inputDesc); 00436 if( found != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00437 { 00438 inputDesc = new CSqlOdbcDesc(); 00439 ipd_.insert(ipd_.end(),inputDesc); 00440 //Initialize inputDescriptor 00441 DataType destType=getCSqlType(valueType); 00442 inputDesc->col_ = parameterNumber; 00443 inputDesc->paramType_ = inputOutputType; 00444 inputDesc->cType_ = valueType; 00445 inputDesc->sqlType_ = parameterType; 00446 inputDesc->dataPtr_= NULL; 00447 //getInputBuffer(&inputDesc->dataPtr_,destType,(SQLUINTEGER)bufferLength); 00448 inputDesc->length_ = (SQLUINTEGER) bufferLength; 00449 inputDesc->precision_ = (short)lengthPrecision; 00450 inputDesc->scale_ = parameterScale; 00451 inputDesc->indPtr_ = (SQLPOINTER) ind; 00452 } 00453 //isParamBound_ = false; 00454 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00455 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLCloseCursor | ( | ) |
Definition at line 887 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLCloseCursor(), AbsSqlStatement::close(), err_, fsqlStmt_, NO_ERR, S3, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
00888 { 00889 // Start with NO_ERR 00890 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00891 00892 // Can we proceed ? 00893 if( chkStateForSQLCloseCursor() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00894 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00895 00896 // Close the cursor 00897 fsqlStmt_->close(); 00898 state_ = S3; 00899 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00900 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLColAttribute | ( | SQLUSMALLINT | columnNumber, | |
| SQLUSMALLINT | fieldIdentifier, | |||
| SQLPOINTER | characterAttributePtr, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT | bufferLength, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | stringLengthPtr, | |||
| SQLPOINTER | numericAttributePtr | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 1213 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLDescribeCol(), err_, ERROR_COLNUM, ERROR_DATATRUNC, FieldInfo::fldName, fsqlStmt_, AbsSqlStatement::getProjFldInfo(), getSQLType(), getSQLTypeName(), AbsSqlStatement::isSelect(), FieldInfo::length, NO_ERR, AbsSqlStatement::noOfProjFields(), CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ATTR_READWRITE_UNKNOWN, SQL_BINARY, SQL_BIT, SQL_CHAR, SQL_COLUMN_COUNT, SQL_COLUMN_LENGTH, SQL_COLUMN_NAME, SQL_COLUMN_NULLABLE, SQL_COLUMN_PRECISION, SQL_COLUMN_SCALE, SQL_COLUMN_TYPE, SQL_DATE, SQL_DESC_AUTO_UNIQUE_VALUE, SQL_DESC_CASE_SENSITIVE, SQL_DESC_COUNT, SQL_DESC_FIXED_PREC_SCALE, SQL_DESC_LENGTH, SQL_DESC_NAME, SQL_DESC_NULLABLE, SQL_DESC_PRECISION, SQL_DESC_SCALE, SQL_DESC_SEARCHABLE, SQL_DESC_TYPE, SQL_DESC_TYPE_NAME, SQL_DESC_UNSIGNED, SQL_DESC_UPDATABLE, SQL_ERROR, SQL_FALSE, SQL_PRED_BASIC, SQL_PRED_SEARCHABLE, SQL_SUCCESS, SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO, SQL_TIME, SQL_TIMESTAMP, SQL_TRUE, SQL_VARBINARY, SQL_VARCHAR, and FieldInfo::type.
01220 { 01221 int nameLen; 01222 int type; 01223 int colSize; 01224 int deciDigits; 01225 int isNullable; 01226 01227 // Start with NO_ERR 01228 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 01229 01230 // Can we proceed ? 01231 if( chkStateForSQLDescribeCol() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 01232 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01233 01234 if( columnNumber < 1 ) 01235 { 01236 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 01237 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01238 } 01239 // If DML 01240 if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() == false ) 01241 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01242 01243 FieldInfo *info = new FieldInfo(); 01244 fsqlStmt_->getProjFldInfo(columnNumber, info); 01245 01246 // If SELECT 01247 if(columnNumber > fsqlStmt_->noOfProjFields()) 01248 { 01249 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 01250 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01251 } 01252 switch(fieldIdentifier) 01253 { 01254 case SQL_DESC_NAME: 01255 case SQL_COLUMN_NAME: 01256 if(characterAttributePtr != NULL) 01257 { 01258 strncpy( (char*)characterAttributePtr, (char*)info->fldName, bufferLength); 01259 if(stringLengthPtr != NULL) 01260 *stringLengthPtr=(short)strlen((char*)info->fldName); 01261 } 01262 break; 01263 case SQL_DESC_COUNT: 01264 case SQL_COLUMN_COUNT: 01265 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01266 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=fsqlStmt_->noOfProjFields(); 01267 break; 01268 case SQL_DESC_TYPE: 01269 case SQL_COLUMN_TYPE: 01270 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01271 *(SQLINTEGER *)numericAttributePtr=getSQLType(info->type); 01272 break; 01273 case SQL_DESC_LENGTH: 01274 case SQL_COLUMN_LENGTH: 01275 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01276 { 01277 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(info->type); 01278 *(SQLINTEGER *)numericAttributePtr=(SQLUINTEGER) info->length; 01279 if(sqlType == SQL_CHAR) 01280 *(SQLINTEGER *)numericAttributePtr=*(SQLINTEGER *)numericAttributePtr -1; 01281 } 01282 break; 01283 case SQL_DESC_PRECISION: 01284 case SQL_COLUMN_PRECISION: 01285 /*if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) // CSQL TODO 01286 *(SQLINTEGER *)numericAttributePtr=(SQLSMALLINT) rsMetaData->getPrecision( columnNumber-1 ); */ 01287 break; 01288 case SQL_DESC_SCALE: 01289 case SQL_COLUMN_SCALE: 01290 /*if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) // CSQL TODO 01291 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=(SQLSMALLINT) rsMetaData->getScale( columnNumber-1 );*/ 01292 break; 01293 case SQL_DESC_NULLABLE: 01294 case SQL_COLUMN_NULLABLE: 01295 /*if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) // CSQL TODO 01296 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=(SQLSMALLINT) rsMetaData->isNullable( columnNumber-1 )?SQL_NULLABLE_N:SQL_NO_NULLS_N;*/ 01297 break; 01298 case SQL_DESC_UNSIGNED: 01299 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01300 { 01301 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(info->type); 01302 if((sqlType != SQL_TIME) && (sqlType != SQL_DATE) && (sqlType != SQL_TIMESTAMP) 01303 && (sqlType != SQL_CHAR) && (sqlType != SQL_VARCHAR) && (sqlType != SQL_BINARY) 01304 && (sqlType != SQL_VARBINARY) && (sqlType != SQL_BIT)) 01305 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_FALSE; 01306 else 01307 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_TRUE; 01308 } 01309 break; 01310 case SQL_DESC_FIXED_PREC_SCALE: 01311 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01312 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_FALSE; 01313 break; 01314 case SQL_DESC_TYPE_NAME: 01315 if(characterAttributePtr != NULL) 01316 { 01317 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(info->type); 01318 strncpy((char*)characterAttributePtr,(char *)(getSQLTypeName(sqlType)),bufferLength); 01319 if(stringLengthPtr != NULL) 01320 *stringLengthPtr=(int)strlen((char *)getSQLTypeName(sqlType)); 01321 } 01322 break; 01323 case SQL_DESC_UPDATABLE: 01324 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01325 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_ATTR_READWRITE_UNKNOWN; 01326 break; 01327 case SQL_DESC_AUTO_UNIQUE_VALUE: 01328 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01329 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_FALSE; 01330 break; 01331 case SQL_DESC_CASE_SENSITIVE: 01332 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01333 { 01334 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(info->type); 01335 if((sqlType != SQL_CHAR) && (sqlType != SQL_VARCHAR)) 01336 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_FALSE; 01337 else 01338 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_TRUE; 01339 } 01340 break; 01341 case SQL_DESC_SEARCHABLE: 01342 if(numericAttributePtr != NULL) 01343 { 01344 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(info->type); 01345 if((sqlType != SQL_CHAR) && (sqlType != SQL_VARCHAR)) 01346 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_PRED_BASIC; 01347 else 01348 *(SQLINTEGER*)numericAttributePtr=SQL_PRED_SEARCHABLE; 01349 } 01350 break; 01351 default: 01352 break; 01353 } 01354 if(stringLengthPtr != NULL) 01355 { 01356 if(*stringLengthPtr > bufferLength) 01357 { 01358 err_.set( ERROR_DATATRUNC ); 01359 return( SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO ); 01360 } 01361 } 01362 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 01363 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
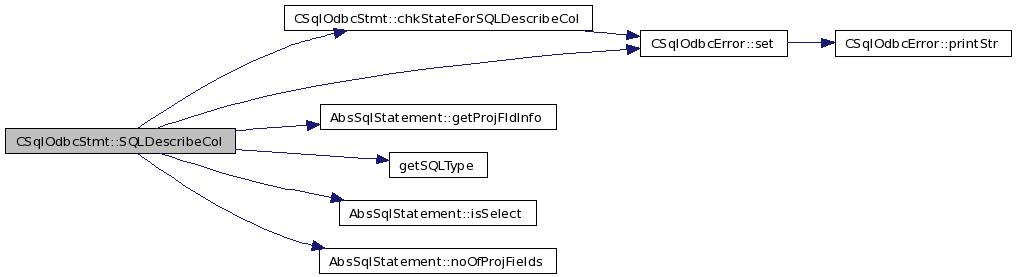
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLDescribeCol | ( | SQLUSMALLINT | columnNumber, | |
| SQLCHAR * | columnName, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT | bufferLength, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | nameLength, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | dataType, | |||
| SQLUINTEGER * | columnSize, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | decimalDigits, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | nullable | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 1108 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLDescribeCol(), err_, ERROR_COLNUM, ERROR_DATATRUNC, FieldInfo::fldName, fsqlStmt_, AbsSqlStatement::getProjFldInfo(), getSQLType(), AbsSqlStatement::isSelect(), FieldInfo::length, NO_ERR, AbsSqlStatement::noOfProjFields(), CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_CHAR, SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO, and FieldInfo::type.
01117 { 01118 int nameLen; 01119 int type; 01120 int colSize; 01121 int deciDigits; 01122 int isNullable; 01123 01124 // Start with NO_ERR 01125 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 01126 01127 // Can we proceed ? 01128 if( chkStateForSQLDescribeCol() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 01129 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01130 01131 if( columnNumber < 1 ) 01132 { 01133 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 01134 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01135 } 01136 01137 // If DML 01138 if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() == false ) 01139 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01140 01141 // If SELECT 01142 if(columnNumber > fsqlStmt_->noOfProjFields()) 01143 { 01144 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 01145 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01146 } 01147 if(columnName == NULL) { 01148 err_.set( ERROR_COLNUM ); 01149 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01150 } 01151 FieldInfo *info = new FieldInfo(); 01152 fsqlStmt_->getProjFldInfo(columnNumber, info); 01153 strncpy( (char*)columnName, (char*)info->fldName, bufferLength ); 01154 if(nameLength != NULL) 01155 *nameLength=(short)strlen((const char*)info->fldName); // HARDCODED - TO DO, need support for n/w layer & sql layer 01156 if(dataType != NULL) 01157 *dataType = (SQLSMALLINT) getSQLType(info->type); // Need to convert from SQL<->ODBC - TO DO 01158 if(columnSize != NULL) 01159 { 01160 *columnSize = (SQLUINTEGER) info->length; 01161 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(info->type); 01162 if(sqlType == SQL_CHAR ) 01163 *columnSize = *columnSize -1; 01164 } 01165 01166 /*if(decimalDigits != NULL) // CSQL TODO 01167 *decimalDigits = (SQLSMALLINT) fsqlStmt_->getPrecision( columnNumber-1 ); 01168 if(nullable != NULL) 01169 *nullable = rsMetaData->isNullable( columnNumber-1 )?SQL_NULLABLE_N:SQL_NO_NULLS_N; */ 01170 if(strlen((char*)info->fldName) > bufferLength) 01171 { 01172 err_.set( ERROR_DATATRUNC ); 01173 return( SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO ); 01174 } 01175 else 01176 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 01177 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
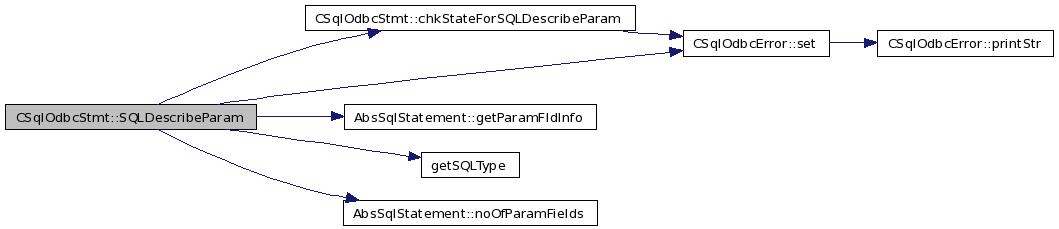
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLDescribeParam | ( | SQLUSMALLINT | paramNumber, | |
| SQLSMALLINT * | dataType, | |||
| SQLUINTEGER * | paramSize, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | decimalDigits, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | isNullable | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 1407 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLDescribeParam(), err_, ERROR_PARAMNUM, fsqlStmt_, AbsSqlStatement::getParamFldInfo(), getSQLType(), FieldInfo::length, NO_ERR, AbsSqlStatement::noOfParamFields(), OK, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_CHAR, SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and FieldInfo::type.
01413 { 01414 01415 // Start with NO_ERR 01416 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 01417 01418 // Can we proceed ? 01419 if( chkStateForSQLDescribeParam() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 01420 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01421 01422 if( paramNumber < 1 ) 01423 { 01424 err_.set( ERROR_PARAMNUM); 01425 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01426 } 01427 01428 //CSqlOdbcError::printDbg("proxy:stmt:getMetaData"); 01429 //CSqlParamMetaData *paramMetaData = fsqlStmt_->getParamMetaData(); 01430 if(paramNumber > fsqlStmt_->noOfParamFields()) 01431 { 01432 err_.set( ERROR_PARAMNUM ); 01433 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01434 } 01435 01436 FieldInfo *finfo = new FieldInfo(); 01437 if( fsqlStmt_->getParamFldInfo( paramNumber-1, finfo ) != OK ) return( SQL_ERROR ); 01438 if(dataType != NULL) 01439 *dataType = (SQLSMALLINT) getSQLType(finfo->type); 01440 if(paramSize != NULL) 01441 { 01442 *paramSize = (SQLUINTEGER) finfo->length; 01443 SQLSMALLINT sqlType=getSQLType(finfo->type); 01444 if(sqlType == SQL_CHAR ) 01445 *paramSize= *paramSize -1; 01446 } 01447 /*if(decimalDigits != NULL) // CSQL TODO 01448 *decimalDigits = (SQLSMALLINT) paramMetaData->getPrecision( paramNumber-1 ); 01449 if(isNullable != NULL) 01450 *isNullable = paramMetaData->isNullable( paramNumber-1 )?SQL_NULLABLE_N:SQL_NO_NULLS_N;*/ 01451 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 01452 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
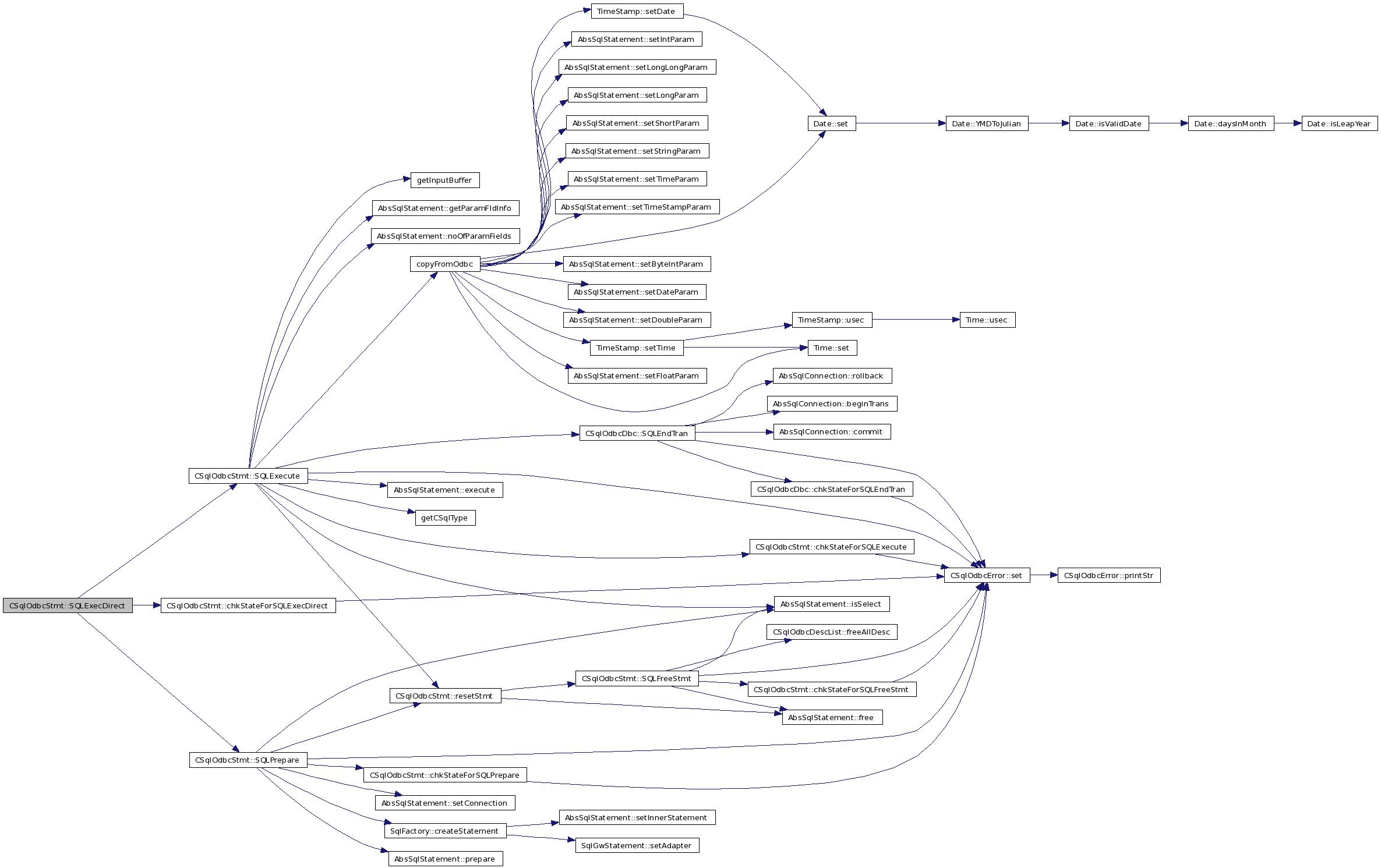
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLExecDirect | ( | SQLCHAR * | statementText, | |
| SQLINTEGER | textLength | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 699 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLExecDirect(), isPrepared_, SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, SQLExecute(), and SQLPrepare().
00702 { 00703 SQLRETURN ret; 00704 00705 // Can we proceed ? 00706 if( chkStateForSQLExecDirect() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00707 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00708 00709 // SQLExecDirect = SQLPrepare + SQLExecute. 00710 if( SQLPrepare( statementText, textLength ) != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00711 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00712 00713 ret = SQLExecute(); 00714 isPrepared_ = false; // Set Stmt as non-prepared stmt. 00715 00716 if( ret != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00717 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00718 00719 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00720 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLExecute | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 549 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References apd_, CSqlOdbcDbc::autoCommit_, C6, chkStateForSQLExecute(), copyFromOdbc(), CSqlOdbcDesc::dataPtr_, err_, ERROR_BUFLEN, ERROR_GENERAL, AbsSqlStatement::execute(), fsqlStmt_, getCSqlType(), getInputBuffer(), AbsSqlStatement::getParamFldInfo(), ipd_, isPrepared_, AbsSqlStatement::isSelect(), NO_ERR, AbsSqlStatement::noOfParamFields(), OK, parentDbc_, resetStmt(), rowsAffected_, S2, S4, S5, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, SQL_COMMIT, SQL_ERROR, SQL_NULL_DATA, SQL_SUCCESS, CSqlOdbcDbc::SQLEndTran(), CSqlOdbcDbc::state_, state_, typeBinary, typeString, and typeUnknown.
Referenced by SQLExecDirect().
00550 { 00551 // Start with NO_ERR 00552 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00553 00554 // Can we proceed ? 00555 if( chkStateForSQLExecute() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00556 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00557 00558 if( fsqlStmt_->noOfParamFields() > 0 ) 00559 { 00560 00561 // Iterate through all apd_; 00562 CSqlOdbcDesc *appParamDesc; 00563 CSqlOdbcDescList::iterator apdIter; 00564 apdIter = apd_.begin(); 00565 CSqlOdbcDesc *csqlParamDesc; 00566 CSqlOdbcDescList::iterator ipdIter; 00567 ipdIter = ipd_.begin(); 00568 00569 //Get the source and the destination type 00570 DataType sourceType = typeUnknown,destType = typeUnknown; 00571 int paramNum=1,sourceLength=-1,destLength=-1; 00572 bool nullFlag=false; 00573 00574 while( (apdIter != apd_.end()) || (ipdIter != ipd_.end()) ) 00575 { 00576 appParamDesc=*apdIter; 00577 csqlParamDesc=*ipdIter; 00578 if((paramNum) <= fsqlStmt_->noOfParamFields()) 00579 { 00580 FieldInfo *finfo = new FieldInfo(); 00581 if( fsqlStmt_->getParamFldInfo(paramNum, finfo ) != OK ) return( SQL_ERROR ); 00582 sourceType=getCSqlType(appParamDesc->cType_); 00583 destType=finfo->type; 00584 sourceLength=(int)appParamDesc->length_; 00585 destLength=finfo->length; 00586 delete finfo; 00587 if(sourceType != typeUnknown && destType != typeUnknown) 00588 { 00589 //Check if NULL is inserted 00590 if((appParamDesc->indPtr_ != NULL ) && (*(SQLINTEGER *)appParamDesc->indPtr_) == SQL_NULL_DATA) 00591 { 00592 nullFlag=true; 00593 //finfo->isNull = true; CSQL TODO - need to understand how to set null 00594 } 00595 else 00596 { 00597 //Only if both types are not the same, then we need to copy it onto intermediate buffer 00598 //Else no need 00599 if( (sourceType == typeString || sourceType == typeBinary) && (sourceLength <= 0)) 00600 { 00601 if((appParamDesc->indPtr_!= NULL) && *(SQLINTEGER *)appParamDesc->indPtr_ > 0) 00602 sourceLength=(int)(*(SQLINTEGER *)appParamDesc->indPtr_); 00603 else if (appParamDesc->precision_ > 0) 00604 sourceLength=appParamDesc->precision_; 00605 else 00606 { 00607 err_.set( ERROR_BUFLEN ); 00608 return SQL_ERROR; 00609 } 00610 } 00611 if(destType == typeString) //|| destType == typeVarString) 00612 { 00613 //fsqlStmt_->allocParam(paramNum,sourceLength); // CSQL TODO 00614 destLength=sourceLength; 00615 } 00616 if(sourceType == destType) 00617 //|| (sourceType == typeString && destType == typeVarString) 00618 //|| (sourceType == typeBinary && destType == typeVarBinary)) 00619 { 00620 copyFromOdbc(fsqlStmt_, paramNum, destLength, appParamDesc->dataPtr_, sourceLength,destType); // CSQL TODO 00621 } else 00622 { 00623 getInputBuffer(&csqlParamDesc->dataPtr_ ,sourceType,sourceLength); 00624 copyFromOdbc(fsqlStmt_, paramNum, destLength, appParamDesc->dataPtr_, sourceLength, sourceType); 00625 //convert(sourceType,csqlParamDesc->dataPtr_,destType, fsqlStmt_->getParamPtr( paramNum),sourceLength,destLength); // CSQL TODO 00626 } 00627 } 00628 } 00629 else 00630 { 00631 err_.set(ERROR_GENERAL); 00632 return SQL_ERROR; 00633 } 00634 } 00635 paramNum++; 00636 apdIter++; 00637 ipdIter++; 00638 } 00639 } 00640 00641 00642 // Get the result 00643 int rowsAffected=0; 00644 DbRetVal rv = fsqlStmt_->execute( rowsAffected ); 00645 if( rowsAffected < 0 ) 00646 { 00647 if( isPrepared_ ) state_ = S2; else resetStmt(); 00648 err_.set( ERROR_GENERAL ); 00649 /*switch(rv) 00650 { 00651 case csqlSqlErrOverflow:err_.set(ERROR_OVERFLOW);break; 00652 case csqlSqlErrUnderflow:err_.set(ERROR_UNDERFLOW);break; 00653 case csqlSqlErrTooManyTpl:err_.set(ERROR_MANY_TUP);break; 00654 case csqlSqlErrProjCnt:err_.set(ERROR_NUM_PROJ);break; 00655 case csqlSqlErrStorageAttr:err_.set(ERROR_STORAGE_ATTR);break; 00656 case csqlSqlErrFldCntMismatch:err_.set(ERROR_FLDCNT_MISMATCH);break; 00657 case csqlSqlErrSqlInternal:err_.set(ERROR_SQL_INT);break; 00658 case csqlSqlErrNoMatchKeyFound:err_.set(ERROR_MATCHKEY_NOTFOUND);break; 00659 default: 00660 err_.set( ERROR_GENERAL );break; 00661 } */ 00662 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00663 } 00664 00665 // Set Stmt State 00666 if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() == true ) 00667 { 00668 rowsAffected_ = -1; 00669 state_ = S5; 00670 } 00671 else 00672 { 00673 rowsAffected_ = rowsAffected; 00674 state_ = S4; 00675 } 00676 00677 // Set Dbc State to Transaction Mode. 00678 parentDbc_->state_ = C6; 00679 00680 // AutoCommit Mode 00681 if( parentDbc_->autoCommit_ == SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON ) 00682 parentDbc_->SQLEndTran( SQL_COMMIT ); 00683 00684 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00685 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
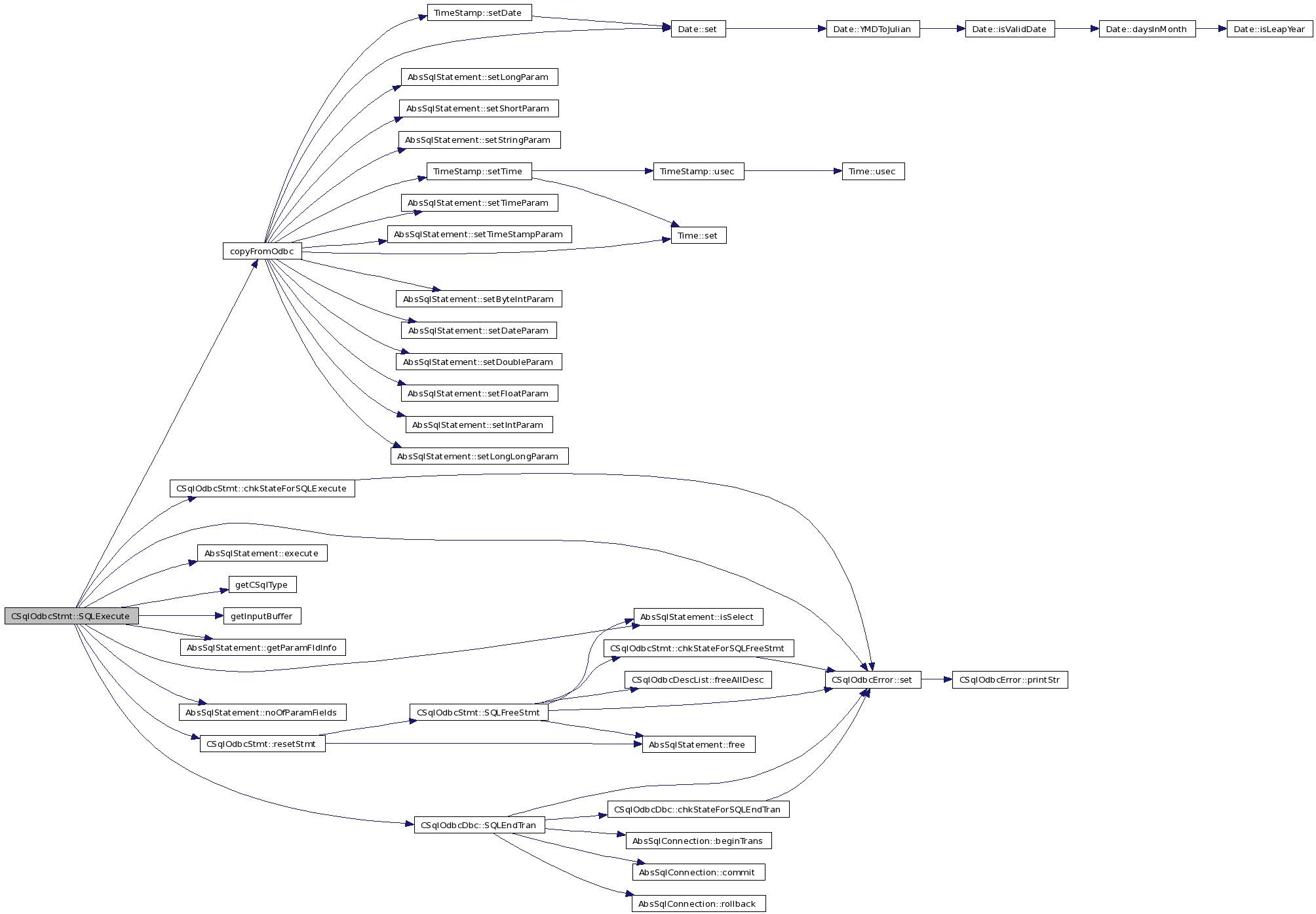
Here is the caller graph for this function:

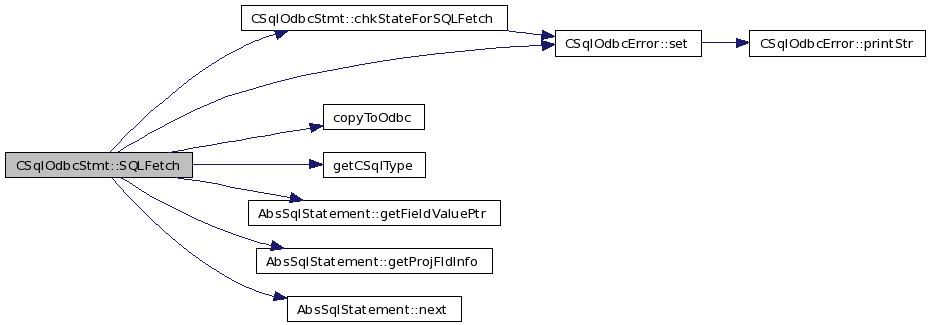
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLFetch | ( | ) |
Definition at line 776 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References ard_, chkStateForSQLFetch(), CSqlOdbcDesc::col_, copyToOdbc(), CSqlOdbcError::csqlErrCode, CSqlOdbcDesc::cType_, CSqlOdbcDesc::dataPtr_, err_, ERROR_DATATRUNC, fsqlStmt_, getCSqlType(), AbsSqlStatement::getFieldValuePtr(), AbsSqlStatement::getProjFldInfo(), CSqlOdbcDesc::indPtr_, ird_, FieldInfo::length, CSqlOdbcDesc::length_, AbsSqlStatement::next(), NO_ERR, rowsAffected_, S6, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_NO_DATA_FOUND, SQL_NULL_DATA, SQL_SUCCESS, SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO, state_, FieldInfo::type, typeString, and typeUnknown.
00777 { 00778 // Start with NO_ERR 00779 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00780 00781 // Can we proceed ? 00782 if( chkStateForSQLFetch() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00783 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00784 00785 void *tuple; 00786 tuple = fsqlStmt_->next(); 00787 00788 if( ! tuple ) // IF Row not found. 00789 { 00790 rowsAffected_ = 0; 00791 state_ = S6; 00792 return( SQL_NO_DATA_FOUND ); 00793 } 00794 /*else if( rowsAffected != SQL_SUCCESS ) // IF Error 00795 { 00796 rowsAffected_ = -1; 00797 err_.set( ERROR_GENERAL ); 00798 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00799 }*/ 00800 else // IF Row found. 00801 { 00802 rowsAffected_ = 1; 00803 00804 // Iterate through all ard_; 00805 CSqlOdbcDesc *appColDesc; 00806 CSqlOdbcDescList::iterator ardIter; 00807 ardIter = ard_.begin(); 00808 //Get the input parameter data 00809 CSqlOdbcDesc *csqlColDesc; 00810 CSqlOdbcDescList::iterator irdIter; 00811 irdIter = ird_.begin(); 00812 00813 DataType sourceType = typeUnknown,destType = typeUnknown; 00814 int colNum=-1,sourceLength=-1,destLength=-1; 00815 SQLINTEGER ind; 00816 void* sourceData = NULL; 00817 FieldInfo *info = new FieldInfo(); 00818 while( (ardIter != ard_.end()) || (irdIter != ird_.end()) ) 00819 { 00820 appColDesc = *ardIter; 00821 csqlColDesc = *irdIter; 00822 00823 colNum = appColDesc->col_ - 1; 00824 fsqlStmt_->getProjFldInfo(colNum, info); 00825 sourceType = info->type; 00826 destType = getCSqlType(appColDesc->cType_); 00827 sourceLength = info->length; 00828 destLength = (int)appColDesc->length_; 00829 00830 if( sourceType != typeUnknown && destType != typeUnknown ) 00831 { 00832 sourceData = fsqlStmt_->getFieldValuePtr( colNum ); 00833 if(sourceData == NULL) 00834 { 00835 if (appColDesc->indPtr_ != NULL) 00836 *((SQLINTEGER *)(appColDesc->indPtr_))=SQL_NULL_DATA; 00837 } 00838 else 00839 { 00840 /*if( sourceType == csqlSqlTvarBinary) 00841 sourceLength=resultSet_->getDataLength(colNum); */ 00842 if (sourceType == typeString ) // CSQL TODO - handle varchar also 00843 { 00844 sourceLength=(int)(strlen((char *) sourceData )); 00845 if(appColDesc->indPtr_ != NULL) 00846 *((SQLINTEGER *)(appColDesc->indPtr_))=copyToOdbc(appColDesc->dataPtr_,destLength, 00847 sourceData,sourceLength, sourceType); 00848 else 00849 copyToOdbc(appColDesc->dataPtr_,destLength,sourceData, 00850 sourceLength, sourceType); 00851 } 00852 else 00853 { 00854 //convert(sourceType,sourceData,destType, csqlColDesc->dataPtr_,sourceLength,destLength); 00855 if(appColDesc->indPtr_ != NULL) 00856 *((SQLINTEGER *)(appColDesc->indPtr_))= 00857 copyToOdbc(appColDesc->dataPtr_,destLength, sourceData, sourceLength, sourceType); 00858 else 00859 copyToOdbc(appColDesc->dataPtr_,destLength, sourceData, sourceLength, sourceType); 00860 } 00861 00862 // CSQL TODO - handle varstring, binary, varbinary 00863 if( sourceType == typeString && sourceLength > destLength ) 00864 err_.set( ERROR_DATATRUNC ); 00865 } 00866 } 00867 ardIter++; 00868 irdIter++; 00869 } 00870 state_ = S6; 00871 } 00872 if(err_.csqlErrCode == ERROR_DATATRUNC) 00873 return (SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO); 00874 00875 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00876 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Definition at line 71 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References C4, C5, isValidHandle(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_HANDLE_STMT, SQL_INVALID_HANDLE, and SQL_SUCCESS.
Referenced by CSqlOdbcDbc::SQLDisconnect(), SQLFreeHandle(), and SQLFreeStmt().
00073 { 00074 CSqlOdbcStmt *inputStmt = (CSqlOdbcStmt*) inputHandle; 00075 00076 // Is Stmt valid ? 00077 if( isValidHandle( inputStmt, SQL_HANDLE_STMT ) != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00078 return( SQL_INVALID_HANDLE ); 00079 00080 // Can we proceed ? 00081 if( inputStmt->chkStateForSQLFreeHandle() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00082 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00083 00084 // Free resultset 00085 inputStmt->resetStmt(); 00086 00087 // Remove Stmt from Parent Dbc. 00088 std::vector<CSqlOdbcStmt*>::iterator iter; 00089 iter = inputStmt->parentDbc_->stmtList_.begin(); 00090 while( iter != inputStmt->parentDbc_->stmtList_.end() ) 00091 { 00092 if( *iter == inputStmt ) 00093 { 00094 inputStmt->parentDbc_->stmtList_.erase( iter ); 00095 break; 00096 } 00097 iter++; 00098 } 00099 00100 // Set Dbc state_ = no statement. 00101 if( inputStmt->parentDbc_->stmtList_.size() == 0 ) 00102 if( inputStmt->parentDbc_->state_ == C5 ) 00103 inputStmt->parentDbc_->state_ = C4; 00104 00105 inputStmt->handleType_ = -1; // Make object invalid. 00106 delete inputStmt; // Delete Stmt. 00107 00108 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00109 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

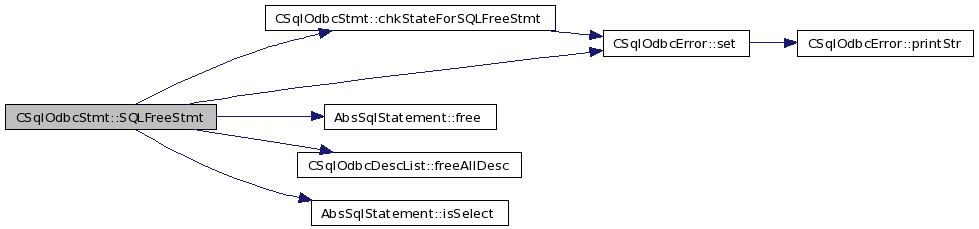
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLFreeStmt | ( | SQLUSMALLINT | option | ) |
Definition at line 126 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References apd_, ard_, chkStateForSQLFreeStmt(), err_, ERROR_OPTRANGE, AbsSqlStatement::free(), CSqlOdbcDescList::freeAllDesc(), fsqlStmt_, ipd_, ird_, isPrepared_, AbsSqlStatement::isSelect(), NO_ERR, S1, S2, S3, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_CLOSE, SQL_ERROR, SQL_RESET_PARAMS, SQL_SUCCESS, SQL_UNBIND, and state_.
Referenced by resetStmt().
00128 { 00129 // Start with NO_ERR 00130 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00131 00132 // Can we proceed 00133 if( chkStateForSQLFreeStmt() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00134 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00135 if (!fsqlStmt_) return (SQL_SUCCESS); 00136 switch( option ) 00137 { 00138 case SQL_CLOSE: // // Free resultset 00139 // if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() == true ) // CSQL 00140 // { 00141 // //CSqlOdbcError::printDbg("proxy:stmt:getResultSet"); 00142 // CSqlResultSet *resultSet_ = fsqlStmt_->getResultSet(); // CSQL 00143 // if( resultSet_ && resultSet_->isOpen() == true ) 00144 // { 00145 // resultSet_->close(); 00146 // } 00147 // } 00148 00149 // cursor states 00150 if( isPrepared_ ) 00151 { 00152 if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() == true ) // CSQL 00153 state_ = S3; // With Cursor 00154 else 00155 state_ = S2; // Without Cursor 00156 } 00157 else 00158 { 00159 ard_.freeAllDesc(); 00160 apd_.freeAllDesc(); 00161 ipd_.freeAllDesc(); 00162 ird_.freeAllDesc(); 00163 fsqlStmt_->free(); // CSQL 00164 state_ = S1; 00165 } 00166 00167 break; 00168 00169 case SQL_UNBIND: ard_.freeAllDesc(); 00170 ird_.freeAllDesc(); 00171 break; 00172 00173 case SQL_RESET_PARAMS: apd_.freeAllDesc(); 00174 ipd_.freeAllDesc(); 00175 //isParamBound_ = false; 00176 break; 00177 00178 default: err_.set( ERROR_OPTRANGE ); 00179 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00180 } 00181 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00182 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLGetCursorName | ( | SQLCHAR * | cursorName, | |
| SQLSMALLINT | bufferLength, | |||
| SQLSMALLINT * | nameLength | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 974 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLGetCursorName(), cursorName_, err_, ERROR_DATATRUNC, ERROR_NOCURNAME, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO.
00978 { 00979 // Can we proceed ? 00980 if( chkStateForSQLGetCursorName() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00981 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00982 00983 if( cursorName_[0] == '\0' ) 00984 { 00985 err_.set( ERROR_NOCURNAME ); 00986 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00987 } 00988 00989 // Copy 00990 *nameLength = (short)strlen( (char*) cursorName_ ); 00991 if( *nameLength > bufferLength ) *nameLength = bufferLength; 00992 strncpy( (char*) cursorName, (char*) cursorName_, *nameLength ); 00993 cursorName[ *nameLength ] = '\0'; 00994 00995 // Did truncate ? 00996 if( bufferLength < strlen( (char*) cursorName_ ) ) 00997 { 00998 err_.set( ERROR_DATATRUNC ); 00999 return( SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO ); 01000 } 01001 01002 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 01003 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
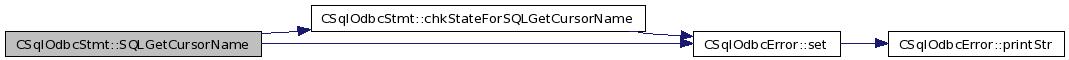
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLNumParams | ( | SQLSMALLINT * | ParameterCountPtr | ) |
Definition at line 1376 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References apd_, chkStateForSQLNumParams(), err_, NO_ERR, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, and SQL_SUCCESS.
01378 { 01379 // Start with NO_ERR 01380 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 01381 01382 // Can we proceed ? 01383 if( chkStateForSQLNumParams() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 01384 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01385 if(ParameterCount == NULL) 01386 return (SQL_ERROR); 01387 *ParameterCount=(int)apd_.size(); 01388 01389 return SQL_SUCCESS; 01390 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

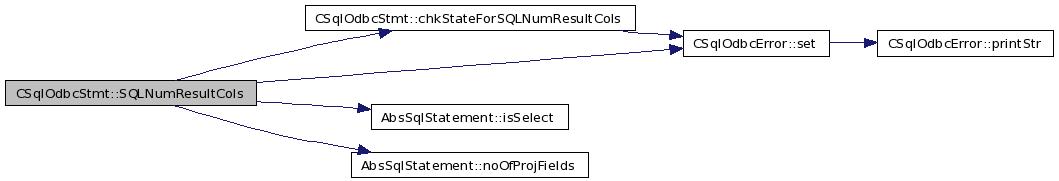
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLNumResultCols | ( | SQLSMALLINT * | columnCount | ) |
Definition at line 1016 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLNumResultCols(), err_, fsqlStmt_, AbsSqlStatement::isSelect(), NO_ERR, AbsSqlStatement::noOfProjFields(), CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, and SQL_SUCCESS.
01018 { 01019 // Start with NO_ERR 01020 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 01021 01022 // Can we proceed ? 01023 if( chkStateForSQLNumResultCols() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 01024 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01025 01026 // If DML 01027 if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() == false ) 01028 { 01029 *columnCount=0; 01030 return (SQL_SUCCESS); 01031 } 01032 01033 // If Select 01034 SQLSMALLINT count = fsqlStmt_->noOfProjFields(); 01035 if( count < 1 ) // Assume atleast one column is projected 01036 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01037 01038 // Fill Column Count 01039 *columnCount = count; 01040 01041 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 01042 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLPrepare | ( | SQLCHAR * | statementText, | |
| SQLINTEGER | textLength | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 470 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLPrepare(), SqlFactory::createStatement(), CSql, CSqlAdapter, CSqlGateway, err_, ERROR_BUFLEN, ERROR_GENERAL, CSqlOdbcDbc::fsqlConn_, fsqlStmt_, isPrepared_, AbsSqlStatement::isSelect(), CSqlOdbcDbc::mode_, NO_ERR, OK, parentDbc_, AbsSqlStatement::prepare(), resetStmt(), S1, S2, S3, CSqlOdbcError::set(), AbsSqlStatement::setConnection(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_NTS, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
Referenced by SQLExecDirect().
00473 { 00474 // Start with NO_ERR 00475 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00476 00477 // Can we proceed ? 00478 if( chkStateForSQLPrepare() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00479 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00480 00481 // Invalid Buffer Length. 00482 if( textLength < 0 && textLength != SQL_NTS ) 00483 { 00484 err_.set( ERROR_BUFLEN ); 00485 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00486 } 00487 00488 // If Stmt is already prepared. 00489 if( state_ >= S2 ) { 00490 resetStmt(); 00491 } 00492 00493 if (parentDbc_->mode_ ==1) 00494 fsqlStmt_ = SqlFactory::createStatement(CSql); 00495 else if (parentDbc_->mode_ ==2) 00496 fsqlStmt_ = SqlFactory::createStatement(CSqlGateway); 00497 else if (parentDbc_->mode_ ==3) 00498 fsqlStmt_ = SqlFactory::createStatement(CSqlAdapter); 00499 fsqlStmt_->setConnection( parentDbc_->fsqlConn_ ); 00500 00501 // Prepare 00502 //CSqlOdbcError::printDbg("proxy:stmt:prepare"); 00503 DbRetVal rv=OK; 00504 if( (rv=fsqlStmt_->prepare( (char*) statementText ))!= OK) // CSQL 00505 { 00506 state_ = S1; 00507 err_.set(ERROR_GENERAL); 00508 /*switch(rv) 00509 { 00510 case csqlSqlErrSchNotFound: err_.set( ERROR_SCHNOTFOUND); break; 00511 case csqlSqlErrTblNotFound: err_.set( ERROR_TBLNOTFOUND); break; 00512 case csqlSqlErrFldNotFound: err_.set( ERROR_NO_COLEXISTS); break; 00513 case csqlSqlErrIndexNotFound: err_.set( ERROR_NO_IDXEXISTS); break; 00514 case csqlSqlErrViewNotFound: err_.set( ERROR_TBLNOTFOUND); break; 00515 case csqlSqlErrTblExists: err_.set( ERROR_TBLEXISTS); break; 00516 case csqlSqlErrFldExists: err_.set( ERROR_COLEXISTS); break; 00517 case csqlSqlErrIndexExists: err_.set( ERROR_IDXEXISTS); break; 00518 case csqlSqlErrViewExists: err_.set( ERROR_TBLEXISTS); break; 00519 case csqlSqlErrTooManyVals:err_.set(ERROR_MANY_VALS);break; 00520 case csqlSqlErrTooFewVals:err_.set(ERROR_FEW_VALS);break; 00521 case csqlSqlErrSqlSyntaxError:err_.set(ERROR_SQL_SYNTAX);break; 00522 case csqlSqlErrIncompatibleType:err_.set(ERROR_TYPE_INCMP);break; 00523 case csqlSqlErrInvalidFormat:err_.set(ERROR_DATA_FORMAT);break; 00524 case csqlSqlErrDuplicateFld:err_.set(ERROR_DUP_COL);break; 00525 case csqlSqlErrSqlInternal:err_.set(ERROR_SQL_INT);break; 00526 default: 00527 }*/ 00528 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00529 } 00530 if( fsqlStmt_->isSelect() != true ) // CSQL 00531 state_ = S2; // With cursor 00532 else 00533 state_ = S3; // Without cursor 00534 00535 //parentDbc_->state_ = C6; 00536 isPrepared_ = true; 00537 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00538 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLRowCount | ( | SQLINTEGER * | rowCount | ) |
Definition at line 1055 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLRowCount(), err_, NO_ERR, rowsAffected_, S4, S5, S6, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_SUCCESS, and state_.
01057 { // TODO 01058 // Start with NO_ERR 01059 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 01060 01061 // Can we proceed ? 01062 if( chkStateForSQLRowCount() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 01063 return( SQL_ERROR ); 01064 01065 if(rowCount == NULL) 01066 return SQL_SUCCESS; 01067 01068 if( state_ == S4 ) // For INSERT/DELETE/UPDATE 01069 *rowCount = (SQLINTEGER) rowsAffected_; 01070 else if( state_ == S5 ) // For SELECT before SQLFetch() 01071 { 01072 *rowCount = (SQLINTEGER) 0; 01073 // CSQL TODO - Think if you really want to do this!!! 01074 01075 /*CSqlOdbcError::printDbg("proxy:stmt:getResultSet"); 01076 CSqlResultSet *resultSet_ = fsqlStmt_.getResultSet(); 01077 if( resultSet_->next() != csqlSqlErrNoTuple ) 01078 *rowCount = (SQLINTEGER) 1; 01079 01080 resultSet_->close(); 01081 resultSet_->open(); */ 01082 } 01083 else if( state_ == S6 ) // For SELECT after SQLFetch(); 01084 *rowCount = (SQLINTEGER) rowsAffected_; 01085 01086 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 01087 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLSetCursorName | ( | SQLCHAR * | cursorName, | |
| SQLSMALLINT | nameLength | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 914 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References chkStateForSQLSetCursorName(), cursorName_, err_, ERROR_CURNAME, ERROR_DUP_CURNAME, ERROR_INVARGVAL, NO_ERR, parentDbc_, CSqlOdbcError::set(), SQL_ERROR, SQL_MAX_CURSOR_NAME_LEN, SQL_NTS, SQL_SUCCESS, and CSqlOdbcDbc::stmtList_.
00917 { 00918 // Start with NO_ERR 00919 err_.set( NO_ERR ); 00920 00921 // Can we proceed ? 00922 if( chkStateForSQLSetCursorName() != SQL_SUCCESS ) 00923 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00924 00925 // Invalid Stmt Length. 00926 if( nameLength < 0 && nameLength != SQL_NTS ) 00927 { 00928 err_.set( ERROR_INVARGVAL ); 00929 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00930 } 00931 00932 // Validate Parameters 00933 if( cursorName == 0 || cursorName[0] == '\0' || strlen( (char*) cursorName ) > SQL_MAX_CURSOR_NAME_LEN || 00934 nameLength > SQL_MAX_CURSOR_NAME_LEN ) 00935 { 00936 err_.set( ERROR_CURNAME ); 00937 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00938 } 00939 00940 // Check for duplicate Name 00941 std::vector<CSqlOdbcStmt*>::iterator iter; 00942 iter = parentDbc_->stmtList_.begin(); 00943 while( iter != parentDbc_->stmtList_.end() ) 00944 { 00945 if( *iter != this ) 00946 { 00947 if( strcmp( (char*) cursorName, (char*) (*iter)->cursorName_ ) == 0 ) 00948 { 00949 err_.set( ERROR_DUP_CURNAME ); 00950 return( SQL_ERROR ); 00951 } 00952 } 00953 iter++; 00954 } 00955 00956 // Copy name 00957 strcpy( (char*) cursorName_, (char*) cursorName ); 00958 00959 return( SQL_SUCCESS ); 00960 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

| SQLRETURN CSqlOdbcStmt::SQLSetStmtAttr | ( | SQLINTEGER | Option, | |
| SQLPOINTER | Value, | |||
| SQLINTEGER | stringLength | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 737 of file odbcStmt.cxx.
References CSqlOdbcError::printDbg(), and SQL_SUCCESS.
00741 { 00742 CSqlOdbcError::printDbg("proxy:stmt:SQLSetStmtAttr"); 00743 //HACK 00744 /*switch(Attribute) 00745 { 00746 //Values: SQL_FETCH_SINGLE_TUPLE or SQL_FETCH_MULTIPLE_TUPLES 00747 //Default is SQL_FETCH_SINGLE_TUPLE. 00748 //In SQL_FETCH_SINGLE_TUPLE mode, only a single tuple 00749 //is sent from server to client in a single packet whatever be 00750 //the packet size. If a tuple size is 50 and network packet size 00751 //is 500, the remaining 450 bytes can also be used to send more 00752 //in a single packet so that in the next SQLFetch call one network 00753 //packet transfer overhead is reduced. 00754 case SQL_FETCH_MODE: 00755 if(state_ <= S5) 00756 //state_ > S5 means Fetch has already started on this statement. 00757 fetchMode_ = (SQLINTEGER)Value; 00758 else 00759 printf("ODBC:Error in setting fetch mode, can't set after fetch is started.\n"); 00760 break; 00761 default: 00762 printf("ODBC: Error, Stmt Option %d is not supported.\n", Attribute); 00763 }*/ 00764 return (SQL_SUCCESS); 00765 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Definition at line 51 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by SQLBindParameter(), SQLExecute(), SQLFreeStmt(), and SQLNumParams().
Definition at line 45 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by SQLBindCol(), SQLFetch(), and SQLFreeStmt().
| SQLCHAR CSqlOdbcStmt::cursorName_[SQL_MAX_CURSOR_NAME_LEN] |
Definition at line 33 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by chkStateForSQLBindCol(), chkStateForSQLBindParameter(), chkStateForSQLCloseCursor(), chkStateForSQLDescribeCol(), chkStateForSQLDescribeParam(), chkStateForSQLExecDirect(), chkStateForSQLExecute(), chkStateForSQLFetch(), chkStateForSQLFreeHandle(), chkStateForSQLFreeStmt(), chkStateForSQLGetCursorName(), chkStateForSQLNumParams(), chkStateForSQLNumResultCols(), chkStateForSQLPrepare(), chkStateForSQLRowCount(), chkStateForSQLSetCursorName(), SQLBindCol(), SQLBindParameter(), SQLCloseCursor(), SQLColAttribute(), SQLDescribeCol(), SQLDescribeParam(), SQLExecute(), SQLFetch(), SQLFreeStmt(), SQLGetCursorName(), SQLNumParams(), SQLNumResultCols(), SQLPrepare(), SQLRowCount(), and SQLSetCursorName().
Definition at line 41 of file odbcStmt.h.
Definition at line 57 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by resetStmt(), SQLCloseCursor(), SQLColAttribute(), SQLDescribeCol(), SQLDescribeParam(), SQLExecute(), SQLFetch(), SQLFreeStmt(), SQLNumResultCols(), and SQLPrepare().
Definition at line 32 of file odbcStmt.h.
Definition at line 54 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by SQLBindParameter(), SQLExecute(), and SQLFreeStmt().
Definition at line 48 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by SQLBindCol(), SQLFetch(), and SQLFreeStmt().
Definition at line 44 of file odbcStmt.h.
Definition at line 39 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by resetStmt(), SQLExecDirect(), SQLExecute(), SQLFreeStmt(), and SQLPrepare().
Definition at line 35 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by SQLExecute(), SQLPrepare(), and SQLSetCursorName().
Definition at line 38 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by SQLExecute(), SQLFetch(), and SQLRowCount().
Definition at line 36 of file odbcStmt.h.
Referenced by chkStateForSQLBindCol(), chkStateForSQLBindParameter(), chkStateForSQLCloseCursor(), chkStateForSQLDescribeCol(), chkStateForSQLDescribeParam(), chkStateForSQLExecDirect(), chkStateForSQLExecute(), chkStateForSQLFetch(), chkStateForSQLFreeHandle(), chkStateForSQLFreeStmt(), chkStateForSQLGetCursorName(), chkStateForSQLNumParams(), chkStateForSQLNumResultCols(), chkStateForSQLPrepare(), chkStateForSQLRowCount(), chkStateForSQLSetCursorName(), resetStmt(), SQLCloseCursor(), SQLExecute(), SQLFetch(), SQLFreeStmt(), SQLPrepare(), and SQLRowCount().
 1.4.7
1.4.7